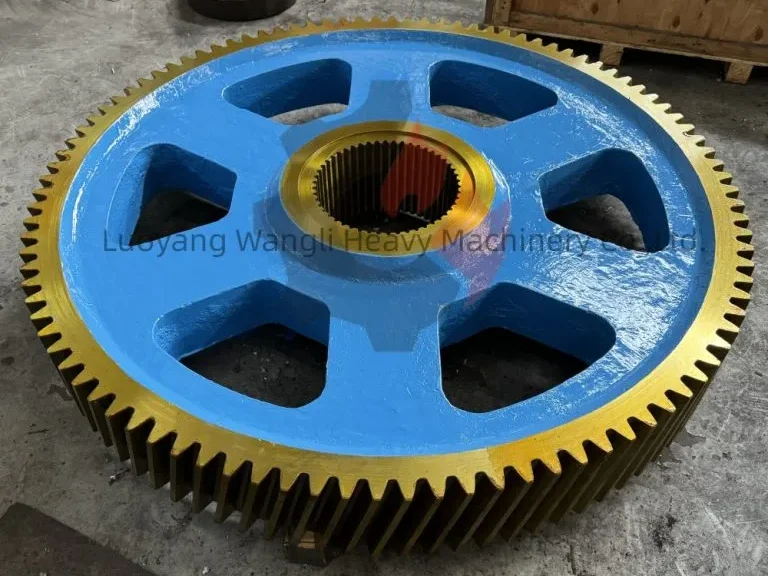
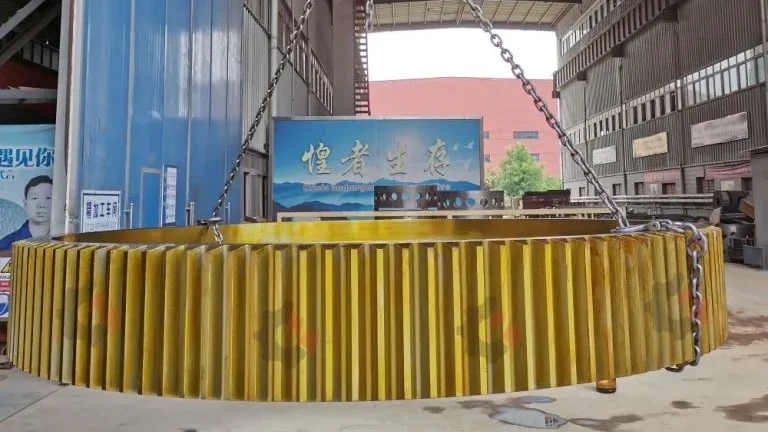
How Large Gears Unleash Colossal Power in Heavy Industries?
In the foundational layers of global industry, where forces are monumental and reliability is non-negotiable, Large Gears serve as the indispensable orchestrators of power. These are not simple components; they are meticulously engineered systems that transform and transmit energy on a gargantuan scale. From the crushing depths of a mine to the soaring heights of a wind turbine, Large Gears provide the controlled, relentless force that drives progress. This exploration goes beyond the surface to uncover the sophisticated engineering, tangible benefits, and expansive applications that make these components the undisputed powerhouses of sectors like mining, energy, oil & gas, and heavy construction.

1.The Engineering Science Behind Large Gears
1.1.What Constitutes a Truly Robust Large Gear?
The term Large Gear signifies a commitment to extreme performance under duress. Its robustness is a calculated outcome of advanced metallurgy, digital design, and precision manufacturing. Modern Large Gears often originate from vacuum-degassed alloy steels, forged to refine their internal grain structure for superior strength and fatigue resistance. The journey from forging to finished gear involves sophisticated processes like CNC gear hobbing followed by precision grinding or honing. This achieves a flawless tooth flank geometry, which is critical for ensuring smooth meshing, optimal load distribution across the entire tooth face, and the minimization of destructive micropitting. The design phase itself leverages Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to simulate stress patterns, allowing engineers to preemptively reinforce areas of potential weakness before a single piece of metal is cut.
1.2.How Do They Achieve Decades-Long Service Life?
The longevity of a Large Gear is engineered into its very being. Beyond material choice, specialized heat treatment is a game-changer. Processes like case carburizing create a hard, wear-resistant surface (the case) while maintaining a tough, shock-absorbing core. This duality allows the gear to resist surface abrasion and subsurface cracking simultaneously. Furthermore, innovative tooth root fillet rolling induces compressive stresses, dramatically enhancing resistance to bending fatigue—a primary failure mode. The integration of advanced lubrication systems, including spray or jet systems that deliver oil directly to the meshing point, ensures a protective film is maintained even under extreme load, reducing wear and dissipating heat efficiently. This holistic approach to durability is what allows Large Gears to operate reliably for decades in punishing environments.
2.Tangible Advantages and Operational Superiority
2.1.Unrivaled Efficiency in Power Transmission
The core value proposition of a premium Large Gear is its ability to transmit maximum power with minimal loss. Modern designs focus on reducing sliding friction and optimizing rolling contact between gear teeth. This is achieved through precise profile modifications (tip and root relief) and the use of high-performance synthetic lubricants. The result is a significant boost in mechanical efficiency, often exceeding 98% per gear mesh stage. For a massive drive system in a mining mill or a wind turbine, this marginal gain translates into megawatts of saved energy annually, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. The Large Gear thus becomes a critical asset in sustainability initiatives, transforming brute force into smart, economical power.
2.2.Custom-Engineered Solutions for Specific Hostile Environments
The one-size-fits-all approach is obsolete in heavy industry. Today’s leading Large Gears are application-specific masterpieces. For offshore wind farms, gears are manufactured with special coatings like nickel-phosphorous to combat saltwater corrosion. In dusty mining operations, labyrinth seals and pressurized gear housings are integrated to exclude abrasive particulates. For high-temperature settings near kilns or furnaces, alloys stable at elevated temperatures are specified. This degree of customization ensures that each Large Gear is not just a part but a co-engineered system element, designed to thrive where standard components would rapidly degrade, thereby maximizing uptime and return on investment.
3.Expansive Applications: The Gear at Industry’s Core
Large Gears are the linchpins in a vast array of critical machinery. Their application scope underscores their versatility and irreplaceability.
3.1.Mining & Minerals: The Grinding Heart
Here, Large Gears face perhaps their toughest challenge. In Semi-Autogenous (SAG) and Ball Mills, a colossal girth gear (often over 10 meters in diameter) is directly coupled to the rotating mill shell. It must endure the relentless impact of thousands of tons of ore and grinding media, shock loads from large rocks, and a constant bath of abrasive slurry. The gear’s performance directly dictates mill throughput and availability, making it the single most critical wear component in the entire concentrator plant. Similarly, in rotary kilns for cement or ore processing, large drive gears facilitate the slow, precise rotation of these massive, heated vessels.
3.2.Power Generation: From Fossil Fuels to Renewable Wind
In thermal power plants, Large Gears are fundamental in coal pulverizers, where they drive grinding tables that crush fuel to a fine powder for combustion. Their reliability ensures consistent boiler feed and stable plant output. The renewable energy sector presents a unique challenge: wind turbine gearboxes. These compact yet immensely powerful assemblies use planetary and helical Large Gears to amplify the slow, high-torque rotation of the blades (15-20 RPM) into the high-speed input (1500-1800 RPM) required by the generator. They operate under variable, unpredictable loads and must exhibit exceptional fatigue life and reliability, as service access is difficult and costly.
3.3.Oil & Gas and Heavy Construction: Power Where It Counts
On drilling rigs, the drawworks system—essentially a giant winch—uses massive Large Gears in its transmission to precisely control the mile-deep descent and hoist of the drill string. Any failure here has severe safety and financial consequences. In heavy construction, slew drives and travel drives in excavators, cranes, and tunnel boring machines rely on large-diameter gears to provide controlled, powerful rotation and movement. These gears enable the precise positioning required for delicate lifts or the relentless force needed for excavation.
4.Comprehensive Application Scenario Table
| Industry Sector | Specific Machinery | Primary Function of Large Gears | Operational Challenge & Gear Response |
| Mining & Minerals | SAG/Ball Mills, Rotary Kilns | Transmit multi-megawatt power to rotate grinding mill or processing kiln. | Challenge: Extreme abrasion, shock loads, contamination. Response: Abrasion-resistant steel, hardened teeth, sealed lubrication. |
| Wind Power | Wind Turbine Gearbox | Amplify low-speed rotor input to high-speed generator output. | Challenge: Variable, cyclical loading, high fatigue stress. Response: Precision-ground profiles, carburized alloys, advanced fatigue design. |
| Oil & Gas | Drawworks, Mud Pumps | Provide controlled torque for hoisting and fluid pumping. | Challenge: Immense static/dynamic loads, need for absolute reliability. Response: High-torque design, rigorous testing, redundant safety features. |
| Thermal Power | Coal Pulverizers, FGD Systems | Drive grinding rollers & absorber fans for fuel/emission processing. | Challenge: High dust, abrasive coal particles, continuous operation. Response: Wear-resistant coatings, robust housing seals, high-temperature alloys. |
| Heavy Machinery | Crawler Crane Drives, Tunnel Boring Machines | Enable travel, slewing, and cutting head rotation. | Challenge: High moment loads, outdoor exposure, precise movement control. Response: Large diameter slew rings, integrated bearing-gear designs, corrosion protection. |
| Marine & Offshore | Ship Propulsion Drives, Crane Booms | Reduce engine RPM to optimal propeller speed or provide lifting motion. | Challenge: Saltwater corrosion, constant vibration, space constraints. Response: Corrosion-resistant coatings, compact planetary designs, vibration analysis. |
5.The Future Trajectory: Intelligence and Advanced Materials
The evolution of Large Gears is accelerating towards greater intelligence and material science breakthroughs. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is leading to “connected gears.” Embedded fiber Bragg grating sensors or acoustic emission sensors can now provide real-time data on tooth root stress, temperature gradients, and lubricant film thickness, enabling true predictive maintenance and preventing catastrophic failures.
Material science is pushing boundaries. Research into advanced powder metallurgy steels offers even finer microstructures for enhanced strength and durability. The exploration of fiber-reinforced composite materials for certain non-critical stages in gearboxes promises significant weight reduction. Furthermore, additive manufacturing (3D printing) is beginning to play a role in producing complex internal cooling channels for gears or prototyping custom tooth forms. As industries demand higher efficiency, lower downtime, and smarter assets, the Large Gear will continue to transform—remaining the quintessential component that not only transmits power but also generates crucial data, ensuring it continues to unleash colossal power for decades to come.
Feel free to contact us for more information or assistance.